Themes, plugins and custom post types can add custom fields and taxonomies to your pages. You can choose which ones WPML should send to translation.
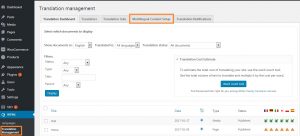
To find the comprehensive list, go to WPML -> Translation Management -> Multilingual Content Setup.
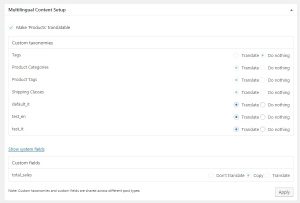
In the Multilingual Content Setup screen, you can find the sections “Custom fields translation”, “Custom posts”, and “Custom taxonomies”.
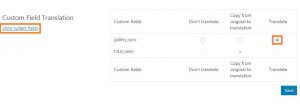
If you don’t see a particular field, click the “Show system fields” link to display the complete list.
If a page/post contains custom fields or taxonomies, in its edit screen WPML will show also a box to configure their translation settings.
WPML allows you to translate, copy or ignore custom fields in translated contents.
You can set up the behaviour for each custom field in the Multilingual Language Setup tab.
- Don’t translate: The custom field will not be copied to the translation. The field and its value will be ignored when creating the translated contents.
- Copy from original to translation: The custom field will be copied to the translation and it will have the same value of the original. It will not be translated.
- Translate: The custom field will be copied to the translation and its value will be translatable.
If you want to translate a custom field or taxonomy, make sure to select the “Translate” option. Next time a document which contains these fields or taxonomies is sent to translation, these will be sent for translation along with it.
For more details, see how to translate custom types and how to set up a WPML language configuration file.
Another more convenient way of handling custom fields is using the Types plugin.
This plugin was created especially for WPML clients, so that they can handle custom post types, taxonomies and fields a lot easier. Types includes a GUI for choosing what’s translatable. It’s a lot more convenient than doing that manually.